Mars water has been discovered
The ESA-Roscosmos ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter has spotted significant amounts of water at the heart of Mars’ dramatic canyon system, Valles Marineris. mars planet.
The water hidden beneath the surface of Mars was discovered by the FREND instrument of the Trace Case Orbiter (TGO), which maps the hydrogen – the amount of water content – to the surface of Mars’ soil.
Although Mars is known to have water, most of it is found as ice in the cold polar regions of the planet. Water ice is not exposed to the surface near the equator because the temperatures here are not cold enough to expose the exposed water ice.
Mars Planet
Tasks, including the ESA’s Mars Express, have been hunting for water near the surface – dust grains in the soil frozen or embedded in minerals – that have detected small volumes at low latitudes on Mars. However, such studies only explored the surface of the planet; There may be deep water stores covered in dust.
“By DGO you can look down up to a meter below this dusty layer and see what’s really going on beneath the surface of Mars – and, more importantly, discover water-filled ‘oases’ that previous instruments could not detect,” says Igor Mitrofanov. Institute of Space Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow, Russia; The primary author of the new study; And FREND (Fine Resolution Epithermal Neutron Detector) Chief Analyst of Neutron Telescope.
Case Orbiter Trace on Mars
Case Orbiter Trace on Mars
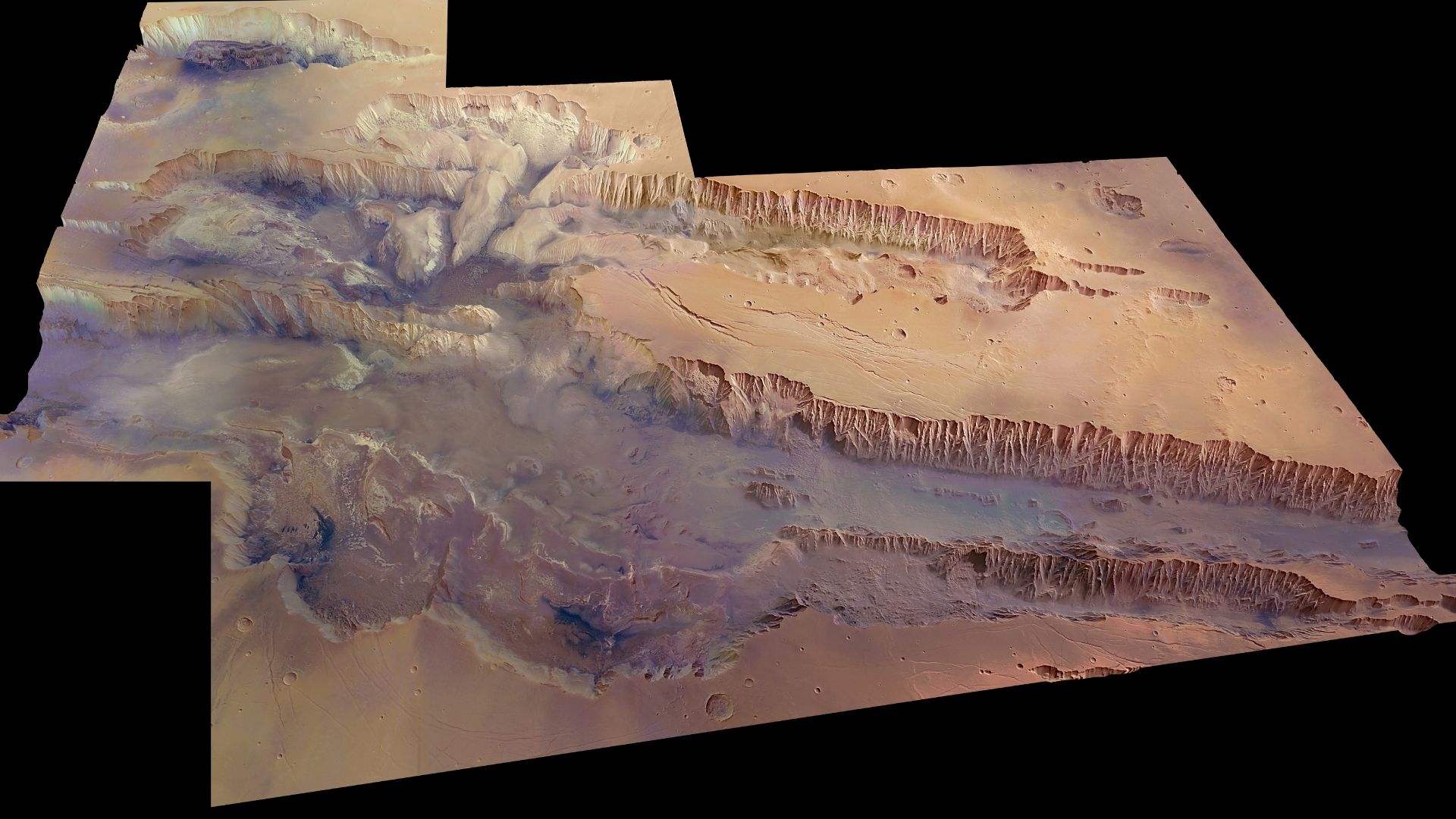
“FREND revealed an unusually high level of hydrogen in the vast Valles Marineris Valley system: 40% of the surface material in this region appears to be water, assuming that the hydrogen we see is bound to water molecules.”
The water-rich region is intertwined with the deep valleys of Candor Chaos, part of the Netherlands and part of the valley system that is considered promising in our hunt for water on Mars.
Mars Future Mission
Since most future missions to Mars are planned to land at low latitudes, finding such a reservoir here is a wonderful opportunity for future exploration.
Although Mars Express finds traces of deep water underground, with pools of deep liquid water beneath the south pole of Mars, these possibilities are up to a few kilometers underground. Found slightly below the surface.
This discovery makes Wallace Marineris a more promising target for future human exploration work. The largest valley in the Solar System, Valles Marineris is the most spectacular landmass on Mars, and is comparable in size to Earth’s Grand Canyon – ten times longer and five times deeper. mars planet.
“This result really proves the success of the joint ESA-Roscosmos ExoMars program,” said Colin Wilson, ESA’s ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter project scientist.
“It’s important to know more about how and where water is on Mars today, to understand what happened to the abundant water on Mars at one time, and to look for possible living conditions, possible signs of past life, and organic matter from the early days of Mars.”
DGO was launched in 2016 as the first of two launches under the Exomars program. The Orbiter will be joined by a European rover, Rosalind Franklin, and the Russian surface base Kazakh in 2022, and everyone will work together to determine if there was ever life on mars planet.